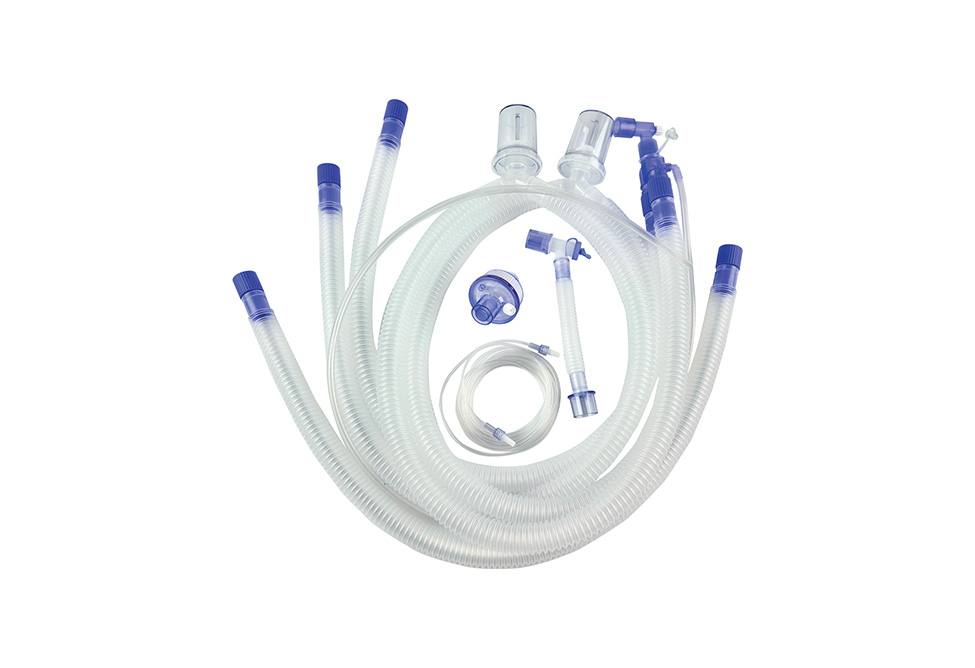
What are the benefits of tracheotomy filter?
Date:2022-11-04
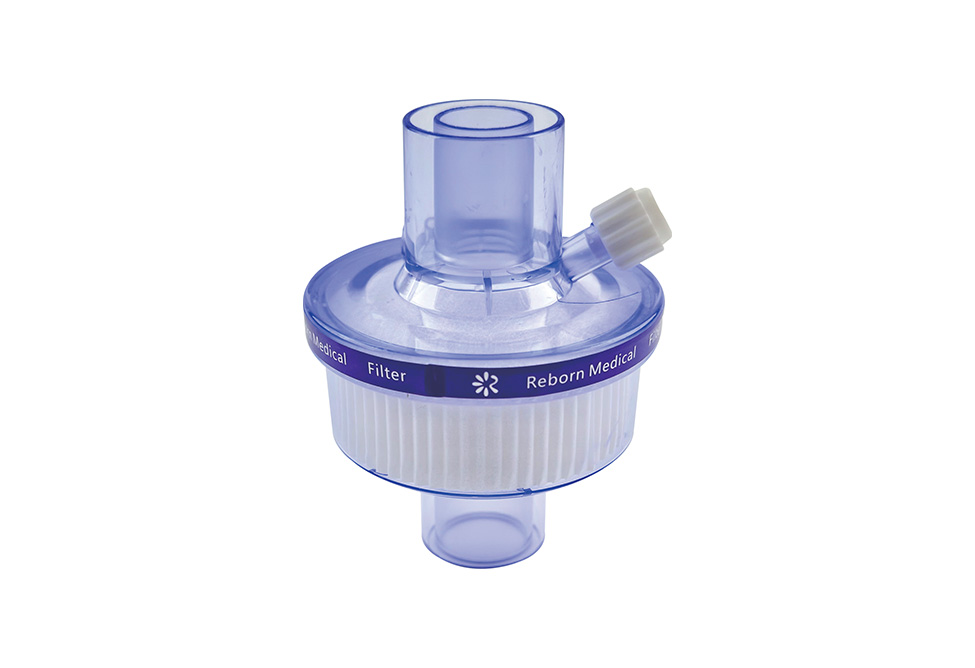
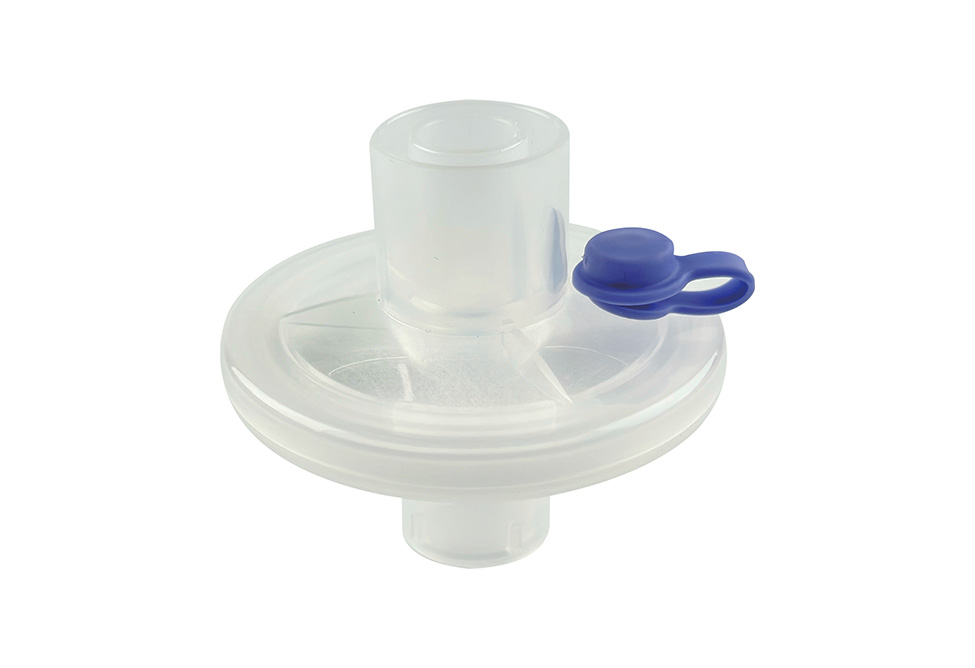
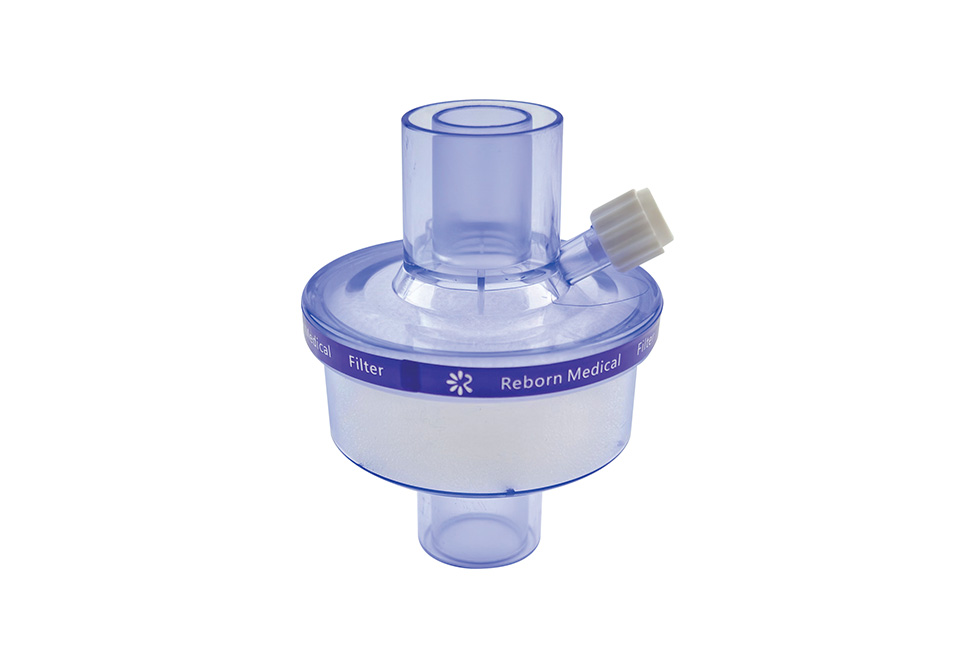
A medical tracheostomy filter is used to keep airborne contaminants and dust from causing damage to the trachea. A filter element comprises two or more layers of net material that are offset from one another. These layers form a micro porous membrane that traps airborne contaminants and dust. The filtering section is placed over the opening 24 of the tracheostomy tube. The filter element is secured to the tracheostomy tube via elastic band 44.
Surgical tracheotomy patients must be managed with a heat and moisture exchanger, a bacterial and viral filter, and a closed endotracheal suctioning system.
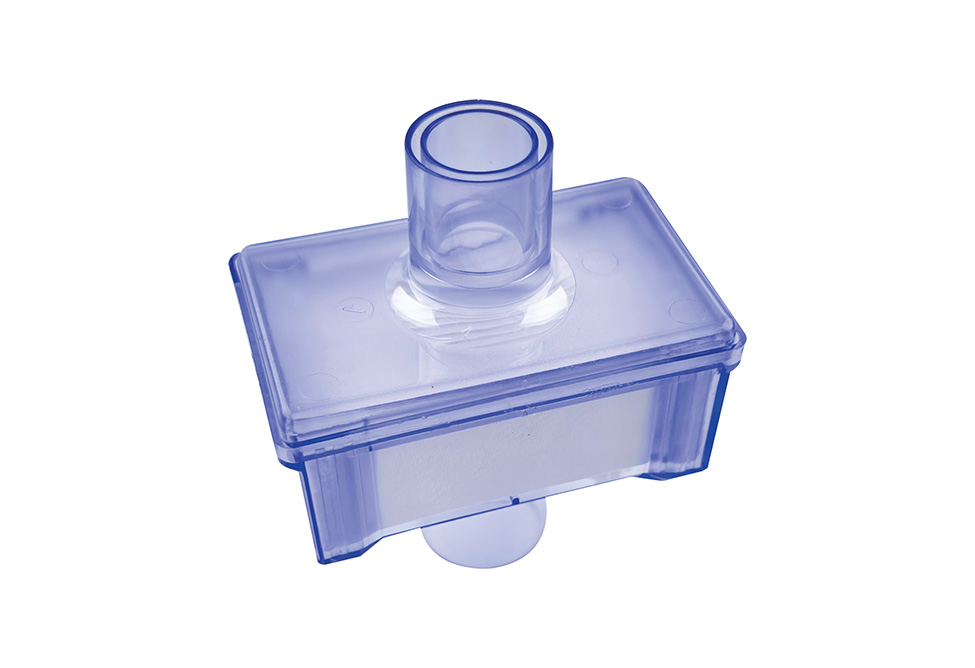
The Heat and Moisture Exchanger (HME) for medical tracheotomy filters use the patient's exhaled moisture to humidify the air. Inhalation of dry air can be harmful to patients. The HME uses the patient's own humidity and warm air to replace the upper airway's function. A HME is a simple device that comprises a plastic cassette/holder and humidifying media. It is placed between the patient's air intake and the outside air. It absorbs moisture from the exhaled air and returns it to the patient's lungs during the patient's inhalation.
HME's also provide some dust removal. The filter mass blocks most of the suspended dust in the air. As the exhaled air cools, it condenses on the filter mass. This allows the exhaled air to be warmed to body temperature. Inhaled air is at the same temperature as the filter mass and takes on the moisture it contacts. This helps to create a more comfortable air environment for patients.
Surgical tracheotomy patients must be managed with a heat and moisture exchanger, a bacterial and viral filter, and a closed endotracheal suctioning system.
The Heat and Moisture Exchanger (HME) for medical tracheotomy filters use the patient's exhaled moisture to humidify the air. Inhalation of dry air can be harmful to patients. The HME uses the patient's own humidity and warm air to replace the upper airway's function. A HME is a simple device that comprises a plastic cassette/holder and humidifying media. It is placed between the patient's air intake and the outside air. It absorbs moisture from the exhaled air and returns it to the patient's lungs during the patient's inhalation.
HME's also provide some dust removal. The filter mass blocks most of the suspended dust in the air. As the exhaled air cools, it condenses on the filter mass. This allows the exhaled air to be warmed to body temperature. Inhaled air is at the same temperature as the filter mass and takes on the moisture it contacts. This helps to create a more comfortable air environment for patients.


 简体中文
简体中文 English
English España
España